Research on heat dissipation methods of electronic components
Research on heat dissipation methods of electronic components is a key technology to ensure the stable operation of equipment, aiming to improve the reliability and service life of electronic equipment.
With the continuous development of science and technology, electronic equipment is used more and more widely.
As an important part of electronic equipment, the performance and reliability of electronic components are crucial to the operation of the entire equipment.
However, since electronic components generate a large amount of heat during operation, if the heat cannot be effectively dissipated and controlled, it will lead to component performance degradation, damage and even safety issues.
Therefore, research on heat dissipation methods of electronic components is of great significance for improving the performance and reliability of electronic equipment.
What is heat dissipation in electronics
The heat dissipation of electronic devices is to control the operating temperature of electronic devices to ensure their working temperature and safety. Since electronic components generate heat during operation, when the heat accumulates to a certain extent, the performance of the electronic components will be reduced or even damaged. Therefore, heat dissipation is one of the important measures to ensure the reliable operation of electronic equipment.
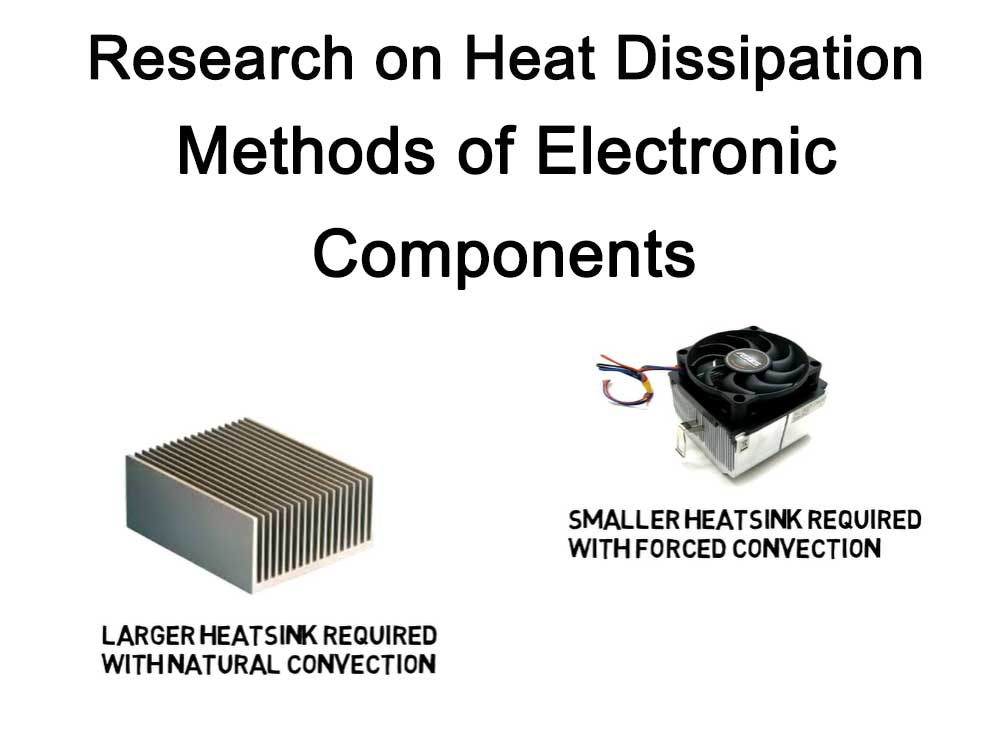
The main purpose of heat dissipation is to effectively dissipate the heat generated by electronic components to the surrounding environment to keep the temperature of the electronic components within the allowable range. The main methods of heat dissipation include natural heat dissipation, forced heat dissipation, liquid heat dissipation, heat pipe heat dissipation, etc. Among them, natural heat dissipation refers to using natural convection to dissipate heat to the surrounding environment; forced heat dissipation refers to dissipating heat to the surrounding environment through forced means such as fans; liquid heat dissipation refers to using liquid coolant to take away heat; heat pipe heat dissipation is Refers to the use of heat pipes to transfer heat to a distant place and then dissipate it.
In electronic components, a heat sink is a device used to absorb, conduct and dissipate the heat generated by electronic components. The main function of the radiator is to prevent electronic components from overheating, prevent component damage, and extend their service life. Radiators can be classified according to material, form and function.
In short, the heat dissipation of electronic devices is one of the important measures to ensure the reliable operation of electronic equipment. It is necessary to choose the appropriate heat dissipation method and radiator according to the actual situation to effectively control the temperature of electronic components.
The necessity of heat dissipation for electronic components
During the working process of electronic components, a large amount of heat will be generated due to the passage of current and the resistance of the component itself.
If this heat cannot be dissipated in time, it will cause the component temperature to rise, thus affecting its performance and reliability.
Under long-term high temperature working environment, electronic components may fail, be damaged, etc., shortening their service life. Therefore, in order to ensure that electronic components can work normally and stably, effective heat dissipation measures must be taken.
Main methods of heat dissipation for electronic components
Natural heat dissipation
Natural heat dissipation refers to the transfer of heat through air convection or radiation without the use of any external auxiliary equipment.
For some electronic components with low power consumption and low heat generation, natural heat dissipation can be used. For example, install components on a well-ventilated heat sink and use natural convection to remove heat.
Forced heat dissipation
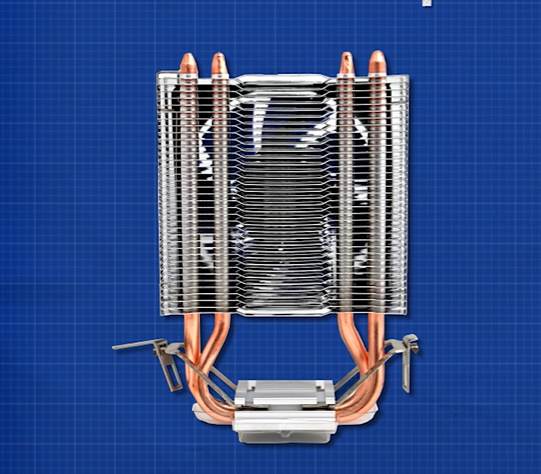
Forced heat dissipation refers to the forced removal of heat through external devices. Commonly used forced cooling methods include cooling fans, heat sinks, etc. The cooling fan can take away the heat through the high-speed rotating fan blades, and the heat sink can use the thermal conductivity of metal to transfer the heat to other parts.
For some electronic components that generate large amounts of heat and need to be quickly dissipated, forced heat dissipation can be used. For example, installing a cooling fan and heat sink on the computer CPU can quickly take away the heat generated by the CPU.

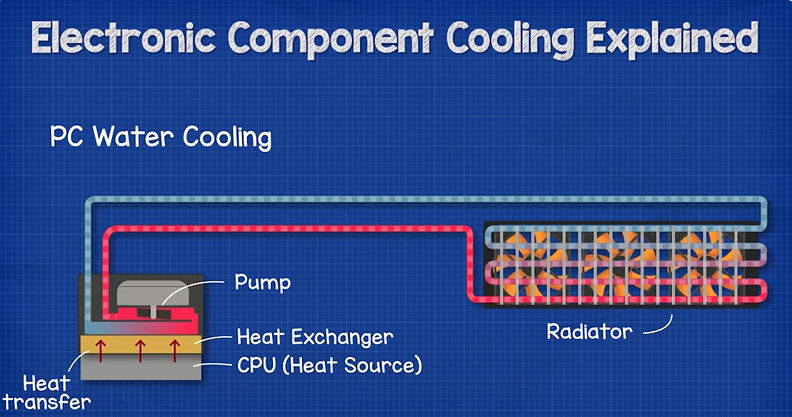
Liquid cooling
Liquid cooling refers to the use of liquid media to transfer heat. Liquid cooling has the advantages of high heat transfer efficiency and good heat dissipation effect, but it also requires relatively complex pipelines and sealing structures.
For some electronic components with high power consumption and high heat generation, liquid cooling can be used to dissipate heat. For example, in large computers or high-power electronic equipment, liquid cooling can be used to remove heat.
Heat pipe heat dissipation
The heat pipe is an efficient heat transfer element. It uses the flow circulation of liquid under capillary action, absorbs heat at the heating end, evaporates, and then condenses at the cooling end to release heat.
Heat pipes have the characteristics of extremely high thermal conductivity, excellent isothermal properties, variability of heat flow density, and reversibility of heat flow direction, and can effectively solve many difficult heat transfer problems.
The use of heat pipe cooling technology in electronic equipment can greatly improve the reliability and service life of the equipment.
Cooling fan
The high-speed rotation of the cooling fan generates a strong air flow and quickly takes away the heat. This method is common in small devices, such as laptops, small servers, etc.
Heat sink
Heat sink is a widely used and effective way of heat dissipation. It uses materials with good thermal conductivity such as metal to transfer the heat generated by components to the heat sink, and then dissipates the heat into the air through the heat sink. Common heat sinks include aluminum and copper.
Heat pipe technology
Heat pipe technology is an efficient heat transfer technology that uses the evaporation and condensation phase change mechanism inside the heat pipe to quickly transfer heat to the condensation end of the heat pipe, and then dissipates the heat through heat sinks and other methods. Heat pipe technology has the advantages of high heat transfer efficiency and high reliability, and is widely used in electronic equipment.
Liquid cooling
Liquid cooling is an efficient heat dissipation method that quickly removes heat through direct contact between liquid and electronic components. Liquid cooling can be divided into two methods: direct cooling and indirect cooling.
Direct cooling is mainly used in high-power density equipment, such as large servers, data centers, etc.; indirect cooling uses an intermediate media system, using liquid modules, thermal conductivity modules, etc. Devices conduct heat transfer in electronic components.
Heat pipe array
Heat pipe array is a large-scale heat dissipation method. Multiple heat pipes are combined and arranged to form a large-area radiator.
It is suitable for high-power equipment such as large servers and data centers. The heat pipe array has the advantages of large heat dissipation area and high heat transfer efficiency, and can effectively solve the heat dissipation problem in high-power equipment.

In general, there are many methods of forced heat dissipation, and the appropriate heat dissipation method needs to be selected according to the actual application scenario and needs. Factors such as power consumption, heat generation, working environment, cost and reliability need to be considered when selecting.
Principles for selecting heat dissipation methods for electronic components
The choice of cooling method depends on the specific application scenario and needs. When choosing, you need to consider the following factors:
Power consumption and heat generation
Choose the appropriate heat dissipation method according to the power consumption and heat generation of electronic components. Components with low power consumption and low heat generation can choose natural heat dissipation or simple forced heat dissipation; components with high power consumption and large heat dissipation need to choose efficient heat dissipation methods such as forced heat dissipation or liquid cooling.
Working environment
Choose the appropriate heat dissipation method according to the working environment of the equipment. In harsh environments (such as high temperature, high humidity, vibration, etc.), you need to choose more reliable heat dissipation methods, such as liquid cooling or heat pipe heat dissipation.
Cost and reliability
On the premise of meeting performance and reliability requirements, lower-cost heat dissipation methods should be selected as much as possible. At the same time, considering the long-term use and maintenance of the equipment, it is also necessary to choose a more reliable heat dissipation method.
Compatibility and maintainability
When selecting a cooling method, you also need to consider its compatibility and maintainability with other parts of the device. It should not have a negative impact on other parts and should be easy to maintain and replace.
Future development trends of heat dissipation technology for electronic components
With the continuous development of science and technology, the heat dissipation technology of electronic components is also constantly improving and improving.
In the future, the heat dissipation technology of electronic components will develop in a more efficient, reliable, and environmentally friendly direction. At the same time, with the continuous emergence of new materials and new processes, it will also bring more possibilities to the heat dissipation technology of electronic components.
For example, new materials such as nanomaterials and graphene have extremely high thermal conductivity and mechanical strength and can be used to make more efficient radiators and heat pipes; new thermal interface materials can reduce thermal resistance and improve thermal conduction efficiency; and intelligent control Technology can automatically adjust the operating status of the cooling system according to the operating status of the equipment to achieve more intelligent management.
In short, the heat dissipation technology of electronic components is one of the important means to ensure the performance and reliability of electronic equipment.
In order to adapt to the evolving needs of electronic equipment, we need to continue to conduct in-depth research and practice new heat dissipation technologies to promote the development and progress of the electronics industry.
Frequently Asked Questions and Answers on Heat Dissipation Methods for Electronic Components
There are many ways to dissipate heat for high-heat devices, including natural heat dissipation, forced heat dissipation, and liquid cooling. Among them, forced heat dissipation can be achieved through cooling fans, heat sinks, heat pipes, etc. For a small number of devices with low heat dissipation, natural heat dissipation can be used, but for devices with large heat dissipation, efficient heat dissipation methods such as forced heat dissipation or liquid cooling are required.
High heat-generating devices refer to electronic components that generate a large amount of heat during operation. Since these components generate a lot of heat, if the heat is not dissipated in time, the temperature of the components will rise, affecting their performance and reliability.
Choosing the right cooling method requires considering multiple factors, including power consumption and heat generation, working environment, cost and reliability. For components with low power consumption and low heat dissipation, you can choose natural heat dissipation or simple forced heat dissipation; for components with high power consumption and high heat dissipation, you need to choose efficient heat dissipation methods such as forced heat dissipation or liquid cooling. At the same time, factors such as the working environment, cost, and reliability of the equipment also need to be considered to select an appropriate heat dissipation method.
When using a radiator, you need to pay attention to the following points: First, make sure that the radiator is in close contact with high-heating components to maximize heat transfer; second, check the integrity of the radiator regularly, and replace it in time if it is damaged; Finally, keep the working environment clean to avoid dust and debris from affecting the heat dissipation effect.
Heat pipe heat dissipation has the advantages of high heat transfer efficiency, excellent isothermal property, heat flow density variability, heat flow direction reversibility, etc., and can effectively solve many difficult heat transfer problems. The use of heat pipe cooling technology in electronic equipment can greatly improve the reliability and service life of the equipment.