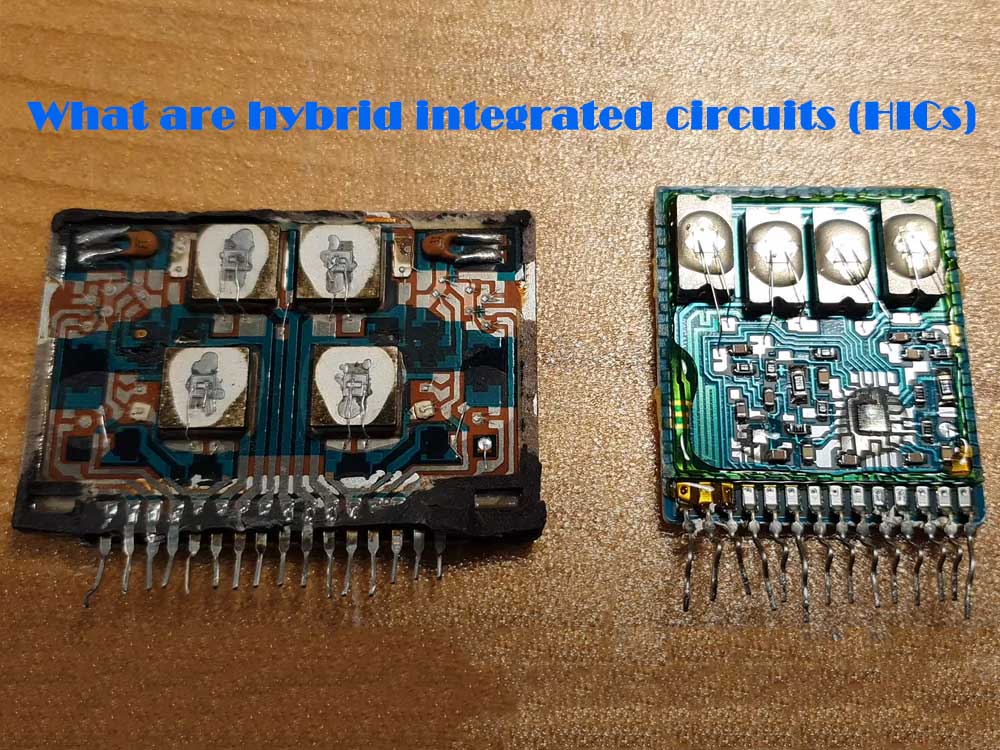
What are hybrid integrated circuits (HICs)
Hybrid integrated circuits (HICs) integrate a variety of electronic components on a substrate to form a complete circuit function.
What is the definition of hybrid integrated circuits (HICs)
Hybrid integrated circuits (HICs) are organic wholes composed of multiple electronic components (active and passive devices) integrated onto the same semiconductor wafer through different processes.
It has the characteristics of miniaturization, lightweight, and high reliability, and is widely used in military, aerospace, electronics and other fields.
What are the disadvantages of hybrid integrated circuits (HICs)
The disadvantages of hybrid integrated circuits mainly include the following aspects:
- Higher cost: The manufacturing of hybrid integrated circuits requires precise control of the size, location and connection methods of each component, so the manufacturing cost is high. At the same time, because it requires multiple independent components to be assembled together, the assembly cost is also high.
- Reliability issues: The components in hybrid integrated circuits are combined together through physical or chemical connections, so reliability issues at the connection points may affect the performance and reliability of the entire circuit.
- Difficulty in maintenance: Since the components in hybrid integrated circuits are closely arranged, it is difficult to replace or repair faulty components.
What are the advantages of hybrid integrated circuits (HICs)
What are the advantages of hybrid integrated circuits hics give? Hybrid integrated circuits (HICs) are microcircuits that integrate multiple electronic components on a single substrate. Its advantages mainly include:
- High assembly density: Hybrid integrated circuits can integrate multiple components in a limited space, thereby increasing the assembly density of the circuit, reducing the volume and weight of the product, and helping to achieve miniaturization and miniaturization of electronic equipment.
- High reliability: Because the components in hybrid integrated circuits are integrated together rather than connected through external connectors, there are fewer connection points and the risk of failure due to poor connections is reduced. At the same time, the components integrated together are not easily affected by the external environment, further improving the reliability of the circuit.
- Good electrical properties: The components in hybrid integrated circuits are made through thin film technology and have good electrical properties, such as low resistance, low capacitance, etc. This results in a circuit with lower signal loss and noise interference, improving circuit performance.
- Flexible design: Hybrid integrated circuits can be customized according to different application requirements using different materials and processes. This gives designers the flexibility to select components, materials and processes based on specific needs to achieve optimal performance and reliability.
- Easy to manufacture and maintain: The manufacturing process of hybrid integrated circuits is relatively simple, and standardization and mass production can be used to reduce production costs. At the same time, the maintenance of hybrid integrated circuits is relatively convenient. Only the entire circuit needs to be tested and repaired, and there is no need to inspect each component one by one.
Hybrid integrated circuits (HICs) have obvious advantages in miniaturization, reliability, electrical performance, design flexibility, and manufacturing maintenance, and are widely used in communications, computers, medical, aerospace and other fields.
What are hybrid integrated circuits examples
A very close look at two hybrid amplifier circuits: An STK type from the late 70s and an SVI 3102 from the late 80s which also includes some exposed integrated circuits. This video explains what hybrid circuits are and how they are different from integrated circuits.
What does Hybrid Integrated Circuits (HICs) SIP mean
SIP (System In a Package) is a system that prioritizes the assembly of multiple active electronic components with different functions, optional passive components, and other components such as MEMS or optical components to achieve certain functions. A single standard package forms a system or subsystem.
SIP integrates multiple functional chips, including processors, memories and other functional chips, into one package to achieve a basically complete function. Architecturally speaking, SIP integrates multiple active electronic components with different functions and optional passive devices into one package to achieve a basically complete function.
SIP uses different chips to be packaged side by side or superimposed, corresponding to SOC (system on chip). The difference is that system-level packaging uses different chips to be packaged side by side or stacked, while SOC is a highly integrated chip product.
In addition, the advantages of SIP include good signal integrity, lower power consumption, and smaller size, making it an efficient and reliable packaging solution that is widely used in various fields, such as communications, computers, etc. , consumer electronics, etc.
What does Hybrid Integrated Circuits (HICs) SOP mean
SOP (Small Out-Line Package) is a common form of component packaging, mainly used in the packaging of integrated circuits. Its pins are led out from both sides of the package in a gull-wing shape (L-shape) and are suitable for surface mount technology (SMT).
SOP packaging has a wide range of applications and can be used in memory LSI, microcomputer circuits and other fields. In areas where the number of pins does not exceed 40, SOP is the most popular surface mount package. The typical pin center distance is 1.27mm (50mil), and others are 0.65mm and 0.5mm. SOP with an assembly height of less than 1.27mm is also called TSOP (Thin SOP).
With the continuous advancement of technology and changing application requirements, the application of SOP packaging has gradually decreased. Now, smaller and more compact packaging forms such as QFP (Quad Flat Package), BGA (Ball Grid Array), etc. have become mainstream.
SOP packaging is a simple, reliable and economical packaging form, mainly suitable for packaging of small and medium-sized integrated circuits.
What does hybrid integrated circuits (HICs) DIP mean
Hybrid integrated circuit DIP (Dual In-line Package) is a type of packaging for electronic components, mainly used for packaging integrated circuits. This package has two rows of equidistant pins, each row of pins are arranged opposite each other, and the spacing between each pin is the same.
In hybrid integrated circuits, DIP packaging is the most common form of packaging, with the number of pins generally not exceeding 100. It is mainly used to insert into a socket or socket on a printed circuit board (PCB) to facilitate connection with a plug or socket. A DIP packaged integrated circuit has two rows of equidistant pins formed along both sides of the package for connection to a plug or socket.
DIP packaging has many advantages, such as its simple packaging structure, high reliability, and strong scalability. Due to its small number of pins, it is very suitable for packaging of small and medium-sized integrated circuits. In addition, the price of DIP packaging is relatively close to the people, which helps reduce production costs.
However, with the development of technology and changing packaging requirements, the application of DIP packaging has gradually decreased. Now, smaller and more compact packaging forms such as QFP (Quad Flat Package), BGA (Ball Grid Array), etc. have become mainstream.
Hybrid integrated circuit DIP is a simple, reliable and economical packaging form, which is mainly suitable for the packaging of small and medium-sized integrated circuits.
What are the packaging methods of hybrid integrated circuits (HICs)
Hybrid integrated circuit is a circuit design method that integrates multiple functional modules into a single chip. The following is a detailed introduction to common hybrid integrated circuit packaging methods:
Dual in-line package (DIP)
This is a traditional package with two pins arranged in parallel. It is suitable for larger chip sizes and is usually manually inserted into a socket. However, due to its relatively large size, it is no longer commonly used.
Small Outline Integrated Circuit (SOIC)
This is a common surface mount packaging method. It has two parallel-arranged straight-in pins, but is smaller and more compact. SOIC packages are widely used in various applications, especially in consumer electronic devices.
Quad Flat Package (QFP)
This is a surface mount package with four neatly arranged pins. It was more common in early chip packaging and was suitable for larger size and higher pin count chips.
Ball Grid Array (BGA)
BGA is a surface mount package with pins arranged in the form of balls on the bottom. These balls are used to connect to pads on a printed circuit board (PCB). Due to the higher pin count, BGA packages can provide better electrical performance and thermal performance.
Land Grid Array (LGA)
LGA is a surface mount package in which the pins are arranged on the bottom in the form of metal pillars through holes instead of pads. This packaging method makes it easier for the pins to connect to the PCB, while providing better electrical performance and heat dissipation performance.
Chip-scale package (CSP)
CSP is a very small package usually used in combination with Ball Grid Array (BGA) or Land Grid Array (LGA). It has very high pin density and compact size, making it suitable for applications requiring a high degree of integration and miniaturization.
These packaging methods are only part of hybrid integrated circuit packaging. There are other special types of packaging methods, such as Quad Flat No Leads (QFN), Thin Small Outline Package (TSOP), etc. Based on specific application needs, design engineers can select the appropriate packaging method to meet functional requirements, space constraints and manufacturing requirements.
Difference analysis between DIP, SOT, SIP and SOP
The following is an analysis of the differences between DIP, SOT, SIP and SOP:
- DIP: Dual in-line package. The pins are drawn from both sides of the package. The packaging materials are plastic and ceramic. DIP is the most popular plug-in package, and its application range includes standard logic IC, memory LSI, microcomputer circuits, etc.
- SOP: One of the surface mount packages, the pins are led out from both sides of the package in a seagull wing shape (L shape). SOP packaging has a wide range of applications. In addition to being used in memory LSI, it is also used in fields with no more than 10 to 40 input and output terminals. SOP is the most widely used surface mount package.
- SIP: System-level packaging, which assembles multiple active electronic components with different functions, optional passive components, and other components such as MEMS or optical components together to form a single standard package that achieves certain functions. A system or subsystem.
In addition, SOT (Surface Mounted Package) is another surface mount package form, with pins leading out from both sides or one side of the package in a round, flat shape, etc. Compared with DIP, SOP and SIP, SOT is smaller in size and suitable for miniaturized electronic products.
In general, these four packaging forms have their own characteristics, and the choice of which packaging form depends on the specific application needs and product requirements.
About Hybrid Integrated Circuits (HICs): Principles, Technologies and Applications
Hybrid Integrated Circuits (HICs for short) is a circuit system that integrates multiple electronic components on a substrate and combines them through physical, chemical or mechanical connections to achieve specific functions.
Compared with traditional integrated circuits, hybrid integrated circuits have higher flexibility, scalability and reliability, so they have been widely used in many fields.
Let’s continue to introduce the principles, technologies and applications of hybrid integrated circuits.
Principles of Hybrid Integrated Circuits (HICs)
The core of hybrid integrated circuits is to integrate different electronic components on the same substrate and realize specific circuit functions through interconnection. These components can be manufactured independently, such as semiconductor chips, resistors, capacitors, etc., or they can be processed directly on the substrate. In a hybrid integrated circuit, components are connected through conductive materials to form a complete circuit system.
The design and manufacturing of hybrid integrated circuits involves knowledge from multiple disciplines, including electronic engineering, materials science, mechanical engineering, etc. In the design, factors such as circuit performance, reliability, power consumption, and manufacturing cost need to be comprehensively considered. During the manufacturing process, the size, location, and connection of each component need to be precisely controlled to ensure the reliability and performance of the circuit.
Hybrid Integrated Circuits (HICs) Technology
- Substrate selection and processing: The substrate is the basis of hybrid integrated circuits, and its selection has an important impact on the performance and reliability of the circuit. Commonly used substrate materials include ceramics, silicon, glass, etc., which need to be selected according to circuit requirements. Substrate processing includes steps such as cleaning, drying, and metallization, and is an important step in the manufacturing process.
- Component manufacturing and assembly: The components in hybrid integrated circuits can be independent or directly processed on the substrate. The manufacturing of components involves a variety of technologies, such as thin film deposition, photolithography, etching, etc. Assembly is the process of placing each component on the substrate according to the design requirements and completing the connection. The accuracy and reliability of assembly have a significant impact on the performance and reliability of the circuit.
- Circuit interconnection and packaging: Each component in a hybrid integrated circuit needs to be connected to each other to form a complete circuit system. Circuit interconnection involves the selection and processing of conductive materials, such as metal wires, solder, etc. Packaging is to protect and seal the completed hybrid integrated circuit to prevent the impact of the external environment on the circuit, while protecting the internal components from damage.
- Testing and Reliability Verification: After manufacturing is completed, the hybrid integrated circuit needs to be tested and reliability verified to ensure that its performance and reliability meet the design requirements. Test content includes functional testing, performance testing, environmental adaptability testing, etc. Reliability verification can be carried out through accelerated aging tests and other methods.
What are hybrid integrated circuits used for
Hybrid integrated circuits have been widely used in many fields due to their flexibility and high reliability. Here are some common application areas:
- Aerospace and Avionics: Hybrid integrated circuits are widely used in the aerospace and aviation fields. Due to their high reliability and stability, they are suitable for harsh environmental conditions. For example, the control systems and navigation systems of aircraft and satellites all use hybrid integrated circuits in large quantities.
- Automotive Electronics: In the field of automotive electronics, hybrid integrated circuits are also widely used. For example, automobile engine control systems, ABS anti-lock braking systems, etc. all use hybrid integrated circuits to implement complex functions.
- Industrial Control and Automation: In the field of industrial control and automation, hybrid integrated circuits are used to implement various control and monitoring functions. For example, industrial robots, automated production lines, etc. all use hybrid integrated circuits.
- Medical Devices: In the field of medical devices, hybrid integrated circuits are widely used due to high requirements for reliability and safety. For example, pacemakers, medical sensors, etc. all use hybrid integrated circuits to implement complex functions.
- Communication and network equipment: In the field of communication and network equipment, hybrid integrated circuits are used to implement various signal processing and transmission functions. For example, mobile phones, routers, switches, etc. all use hybrid integrated circuits to achieve high-speed data transmission and signal processing.
Future development trends and challenges
With the continuous development of science and technology, the technology and applications of hybrid integrated circuits are also constantly improving. In the future, the development of hybrid integrated circuits will mainly focus on the following aspects:
- High performance and high reliability: With the continuous expansion of applications and the continuous improvement of demands, the requirements for the performance and reliability of hybrid integrated circuits are becoming higher and higher. The future will require the development of more advanced manufacturing and materials technologies to improve circuit performance and reliability.
- Integration and miniaturization: Integration and miniaturization are important trends in the future development of hybrid integrated circuits. By continuously increasing the level of integration and reducing the size of components, circuit volume can be reduced and performance improved. At the same time, miniaturization also helps improve circuit reliability and reduce manufacturing costs.
- Intelligence and automation: Intelligence and automation are also important development directions for hybrid integrated circuits in the future. By introducing artificial intelligence and automation technology, intelligent circuit design and manufacturing processes can be realized, improving production efficiency and product quality.
- Environmental protection and sustainable development: With the increasing emphasis on environmental protection issues, the development of environmentally friendly hybrid integrated circuit manufacturing technology is also an important trend in the future. By using environmentally friendly materials and processes.