China’s Hall sensor is a magnetic sensor based on the Hall effect principle, which plays an important role in many fields.
The following is a detailed introduction to China’s Hall sensor:
Hall effect and Hall sensor principle
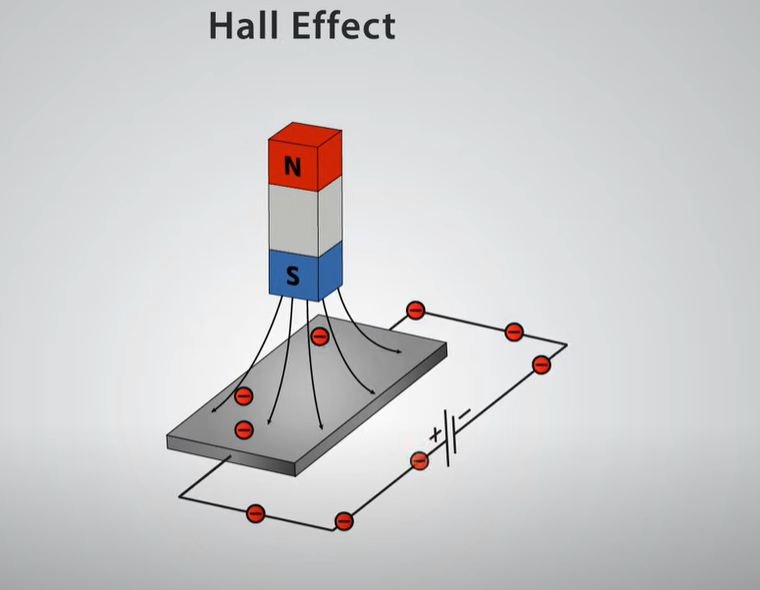
The Hall effect refers to the phenomenon that when charged particles (such as electrons) move in a magnetic field, they will be deflected by the Lorentz force, thereby generating a potential difference (i.e., Hall voltage) on both sides perpendicular to the magnetic field and the direction of the current. This phenomenon was discovered by American physicist Edwin Hall in 1879 and got its name from it.
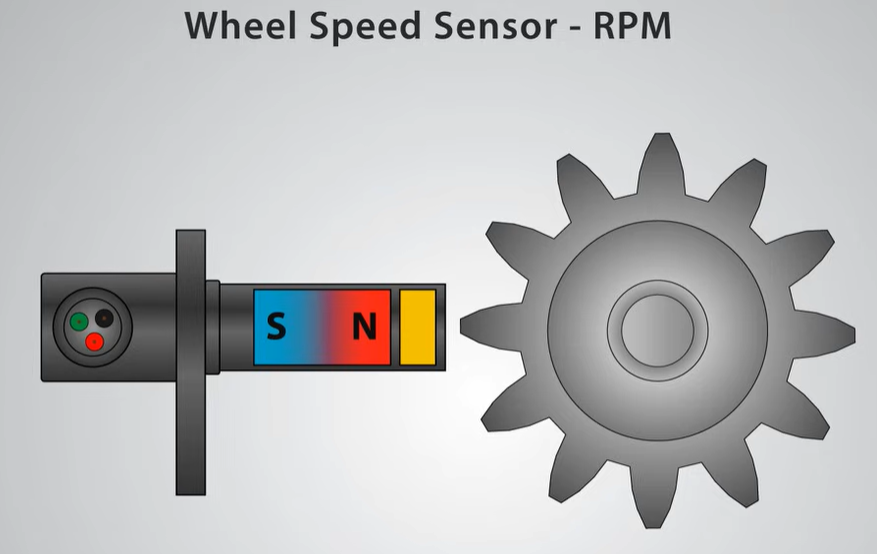
The Hall sensor is a sensor made using the Hall effect principle. It is usually composed of a Hall element and its associated circuits. When a magnetic field acts on a Hall element, a Hall voltage proportional to the magnetic field strength is generated on both sides. By measuring this voltage, the magnetic field can be detected.
Characteristics of Hall sensors
High sensitivity
Hall sensors can detect weak magnetic field changes and have high sensitivity.
Low power consumption
Hall sensors consume less power when working and are suitable for long-term operation.
Non-contact measurement
Hall sensors can use magnetic fields as a medium to achieve non-contact measurement of the measured object, avoiding problems such as mechanical wear and contact resistance.
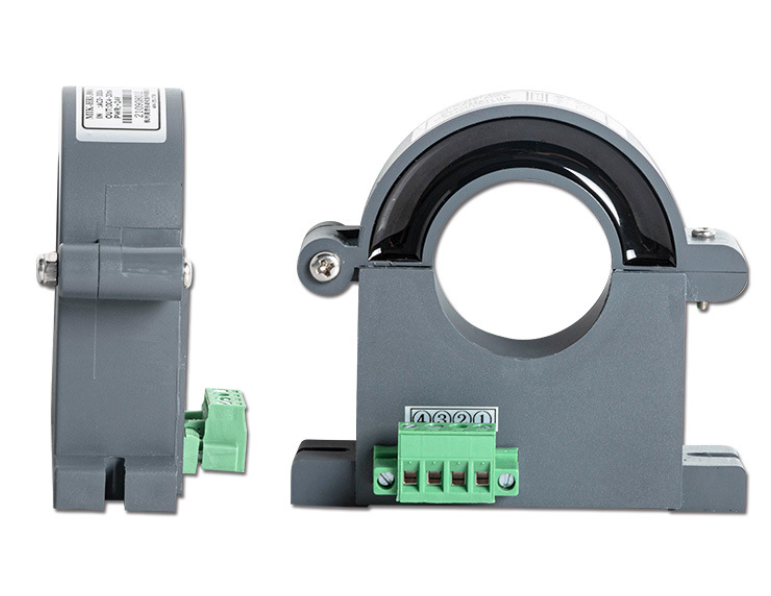
Wide measurement range
Hall sensors can measure current and voltage of various waveforms, including DC, AC and pulse waveforms, and have a wide measurement range.
High precision
In the operating temperature range, the accuracy of Hall sensors is usually better than 1%, which is suitable for various high-precision measurement occasions.
Good electrical isolation
The primary circuit and secondary circuit of the Hall sensor have good electrical isolation performance, which can ensure the safety of measurement.
Application fields of Hall sensors
Due to the above characteristics, Hall sensors have been widely used in China and even around the world. The following are some of the main application fields:
Industrial automation
In the field of industrial automation, Hall sensors are widely used in position detection, speed measurement, current measurement, etc. For example, in brushless motors, Hall sensors can detect the position of permanent magnets to achieve precise control of motors.

Automotive electronics
In automotive electronic systems, Hall sensors are used to detect changes in magnetic fields to monitor and measure the operating parameters of various components of the vehicle.
For example, in power steering and braking systems, Hall sensors can detect changes in magnetic fields to achieve precise control of the system. In addition, Hall sensors are also used in speedometers, tachometers and other instruments to achieve accurate measurement of vehicle speed.
Medical Technology
In the medical field, Hall sensors are used in applications such as magnetic field imaging. For example, in MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), Hall sensors can detect changes in magnetic fields to help doctors obtain image information inside the patient’s body.
Aerospace
In the aerospace field, Hall sensors are used in various high-precision measurement and control systems. For example, in the navigation systems of aircraft and rockets, Hall sensors can detect changes in magnetic fields to achieve precise control of flight attitude.
Other fields
In addition, Hall sensors are also widely used in transportation, communications, electricity, home appliances and other fields.
For example, in the field of electric bicycles, Hall sensors are used to detect information such as motor speed and current; in power systems, Hall sensors are used to detect parameters such as current and voltage.
Development Status of Hall Sensors in China
In recent years, with the rapid development of China’s manufacturing industry and the continuous improvement of scientific and technological innovation capabilities, China’s Hall sensor industry has also made significant progress.
A number of Hall sensor manufacturers with independent R&D capabilities and market competitiveness have emerged in China.
These companies have continuously increased their R&D investment, improved product performance and quality, and gradually broken the monopoly of foreign brands on the high-end market.
At the same time, with the rise and development of emerging technologies such as the Internet of Things and intelligent manufacturing, China’s Hall sensor industry is also facing new development opportunities and challenges.
In the future, China’s Hall sensor industry will continue to strengthen technological innovation and industrial upgrading, promote the development of products in the direction of high-end and intelligent; at the same time, strengthen cooperation and exchanges with the international market to enhance the international competitiveness and influence of China’s Hall sensor industry.
Summary
In summary, China’s Hall sensor is a magnetic sensor based on the Hall effect principle, with the characteristics of high sensitivity, low power consumption, non-contact measurement, etc., and has been widely used in industrial automation, automotive electronics, medical technology, aerospace and other fields.
With the rapid development of China’s manufacturing industry, the continuous improvement of scientific and technological innovation capabilities, and the rise and development of emerging technologies, China’s Hall sensor industry will usher in a broader development prospect.
Buy Hall Sensors from China
E-components.globalbestshopping.com is committed to providing brand marketing services for electronic component manufacturers. We also provide electronic component BOM lists and provide various types of component products for electronic component buyers.
E-components.globalbestshopping.com Electronic Components Website has global professional search engine technology researchers, focusing on providing a one-stop component sales channel platform for electronic component factories, wholesalers, suppliers, and distributors. E-components.globalbestshopping.com is an electronic component search engine optimization technology platform, a professional electronic component technology knowledge base, if you need to know about advertising, please contact us.
If you need to purchase electronic components, please send your requirements and we will reply to you as soon as possible.
In China, Hall sensors, as a sensor based on the Hall effect, are widely used in industries such as industry, electronics, and automobiles. Here are some common questions and answers about Hall sensors in China:
FAQs
A Hall sensor is a sensor based on the Hall effect that is used to detect the presence or strength of a magnetic field. Its working principle is to use the potential difference generated by the movement of charged particles in a magnetic field, and it is made of semiconductor materials such as gallium arsenide GaAs. When a magnetic field is applied to the semiconductor, a Hall voltage proportional to the strength of the magnetic field is generated.
Hall sensors are not produced by a single country, but by many countries around the world. In the Hall sensor supply chain, due to the early start of developed countries, IC design manufacturers in the United States, Japan, the United Kingdom, France and Germany, such as Allegro, Micronas, Melexis, AKM, Infineon and other companies, are leading the update and iteration of global Hall sensor products. At the same time, there are many companies in China that produce Hall sensors and occupy a certain share in the market. Therefore, it can be said that Hall sensors are products jointly produced by many countries around the world.
Hall sensors are widely used in many fields due to their high sensitivity, low power consumption and compact size, including:
Position and motion detection: Detecting motion in brushless motors, angle sensors and speedometers.
Current measurement: Detecting current intensity, such as in current transformers.
Magnetic field imaging: Creating magnetic field maps in medical imaging (MRI) and non-destructive testing (NDT) applications.
Proximity and object detection: Used in proximity switches, door locks and security systems.
Automotive applications: Detecting magnetic fields in automotive electronic systems such as power steering and braking systems.
Hall sensors may encounter the following common faults during use:
Sensor detachment: The sensor may fall off due to loose fixation, resulting in failure to work properly. At this time, materials such as resin can be used to re-fix it.
Lead disconnection: The sensor lead may be disconnected due to long-term use or external force. If the disconnection occurs at the root of the integrated circuit, the entire sensor may need to be replaced; if the disconnection is far away, you can try to re-weld it.
Hall integrated circuit failure: including circuit failure itself and working power supply problems. At this time, you need to determine the source of the fault before repairing or replacing it.
Reduced sensitivity: It may be caused by changes in magnetic field strength, temperature changes, or unstable power supply voltage. It is necessary to adjust the power supply voltage, add a shielding cover, or use temperature compensation technology according to the specific situation.
Improving the stability of the Hall sensor can start from the following aspects:
Choose a suitable power supply voltage: Make sure that the power supply voltage is within the rated voltage range of the Hall sensor.
Add a shielding cover: Reduce the impact of external electromagnetic interference on the sensor.
Use temperature compensation technology: Reduce the impact of temperature on the accuracy of the sensor output signal.
Regular inspection and maintenance: Including checking whether the sensor is damaged or corroded, whether the circuit connection is good, and whether the output signal is normal.
Compared with other types of sensors, Hall sensors have the advantages of non-contact measurement, high precision and high sensitivity. At the same time, their compactness, ruggedness and durability also make them more competitive in various application scenarios. However, different types of sensors have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the specific choice should be based on actual needs and usage environment.
Hall sensors are mainly made of semiconductor materials, such as silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), etc. These materials have good electron mobility and Hall effect characteristics, and are key components for generating Hall potential difference. In addition, packaging materials usually use non-magnetic metals, ceramics or epoxy resins to protect the sensor from interference and damage from the external environment.
Although the Hall effect itself does not directly involve the reaction of chemical elements, the conductive properties of semiconductor materials are closely related to their internal electronic structure and chemical element composition. The conductivity of semiconductor materials is between that of conductors and insulators, and their electronic structure makes them very sensitive to changes in magnetic fields, which can produce a significant Hall effect. Therefore, it can be said that the conductivity of semiconductor materials used in Hall sensors is determined by their chemical element composition and electronic structure.
The application of Hall sensors in the field of chemistry is mainly reflected in the measurement and control of magnetic fields. For example, in electrochemical experiments, Hall sensors can be used to detect changes in magnetic fields in electrolyte solutions, thereby helping researchers to control experimental conditions more accurately. In addition, Hall sensors also play an important role in the fields of magnetic material analysis, magnetic fluid research, and magnetic field-controlled chemical reactors. These applications all take advantage of the Hall sensor’s ability to accurately detect magnetic fields and their changes.
It should be noted that the Hall sensor itself is not directly used for the detection of chemical elements. It is mainly used to measure changes in magnetic fields, rather than directly analyzing the chemical composition or elements in a substance. Therefore, in situations where specific chemical elements or compounds need to be detected, it may be necessary to combine other types of sensors or analytical techniques to achieve this.


