The main difference between capacitors and inductors is their working principle and purpose. Capacitors are mainly used to store electrical energy and play a role in filtering, bypassing and energy storage in circuits; while inductors store magnetic energy by establishing a magnetic field and are mainly used in AC applications such as televisions and radios.
Overview of the Differences Between Capacitors and Inductors
Capacitors and inductors are two important components in electronic components. They play different roles in circuits and have unique working principles and characteristics.
As a component manufacturer, we have an in-depth understanding of the differences and characteristics of capacitors and inductors, and can provide customers with more accurate selection suggestions and technical support.
This article will explain the differences between capacitors and inductors in detail to help readers better understand and apply these two components.
The difference between the definitions and working principles of capacitors and inductors
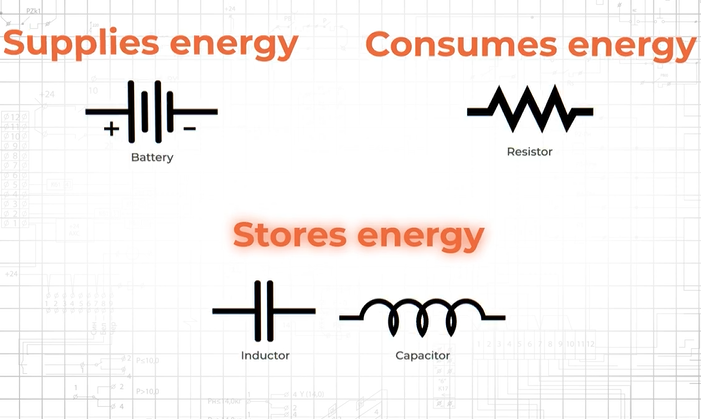
- Capacitor: A capacitor is a component that can store electric charge. It consists of two mutually insulated conductor plates filled with dielectric in between. When a voltage is applied across the capacitor, charges accumulate on the conductor plates, forming an electric field that stores electrical energy. The capacitance of a capacitor is expressed in the unit Farad (F), which determines the capacitor’s ability to store charge.
- Inductor: An inductor is a component that can store magnetic energy. It is made of coils. When current flows through the inductor, a magnetic field is generated within the coil, thereby storing magnetic energy. The size of an inductor is expressed in the unit Henry (H), which determines the inductor’s ability to store magnetic energy.
Analysis of the differences between capacitors and inductors
- Working principle: Capacitors store electrical energy by storing electric charge, while inductors store energy by storing magnetic energy. These two energy storage methods have different physical properties and application scenarios.
- Frequency response: Capacitors are more sensitive to high-frequency signals, while inductors are more sensitive to low-frequency signals. This is because capacitors have less impedance at high frequencies, while inductors have greater impedance at low frequencies.
- Impedance characteristics: The impedance of a capacitor is inversely proportional to frequency, while the impedance of an inductor is directly proportional to frequency. This means that at low frequencies, the impedance of the capacitor is larger and the impedance of the inductor is smaller; at high frequencies, the opposite is true.
- Charge and discharge characteristics: Capacitors have fast charge and discharge characteristics, while the charge and discharge process of inductors is relatively slow. This makes capacitors more suitable for applications that require fast response, such as filtering, coupling, etc.; while inductors are suitable for applications that require smooth current or energy storage.
- Application fields: Since capacitors and inductors have different working principles and characteristics, their application fields in practical applications are also different. Capacitors are widely used in power supply filtering, signal coupling, oscillation circuits and other fields; while inductors are often used in power supply filtering, power factor correction, transformers and other fields.
Capacitor and inductor selection and application recommendations
- Selection suggestions: When selecting capacitors or inductors, comprehensive considerations need to be made based on the actual circuit requirements and performance indicators. For example, where fast charge and discharge are required, capacitors with low internal resistance and high charge and discharge speed should be selected; where smooth current is required, inductors with larger inductance and lower DC resistance should be selected.
- Application suggestions: In practical applications, the combined use of capacitors and inductors can achieve optimal circuit design. For example, in a power supply filter circuit, using both a capacitor and an inductor can more effectively filter out high-frequency noise and ripple in the power supply; in an oscillation circuit, oscillation signals of different frequencies can be achieved by adjusting the parameters of the capacitor and inductor. output.
Conclusion on the difference between capacitors and inductors
Through the detailed explanation of this article, we can clearly see the significant differences between capacitors and inductors in terms of working principles, frequency response, impedance characteristics, charge and discharge characteristics, and application fields.
As a component manufacturer, we hope to help engineers better understand and apply these two important electronic components by providing accurate technical information and selection suggestions.
In the future technological development, we will continue to pay attention to the research progress and application innovation of capacitors and inductors, and provide customers with better products and services.
