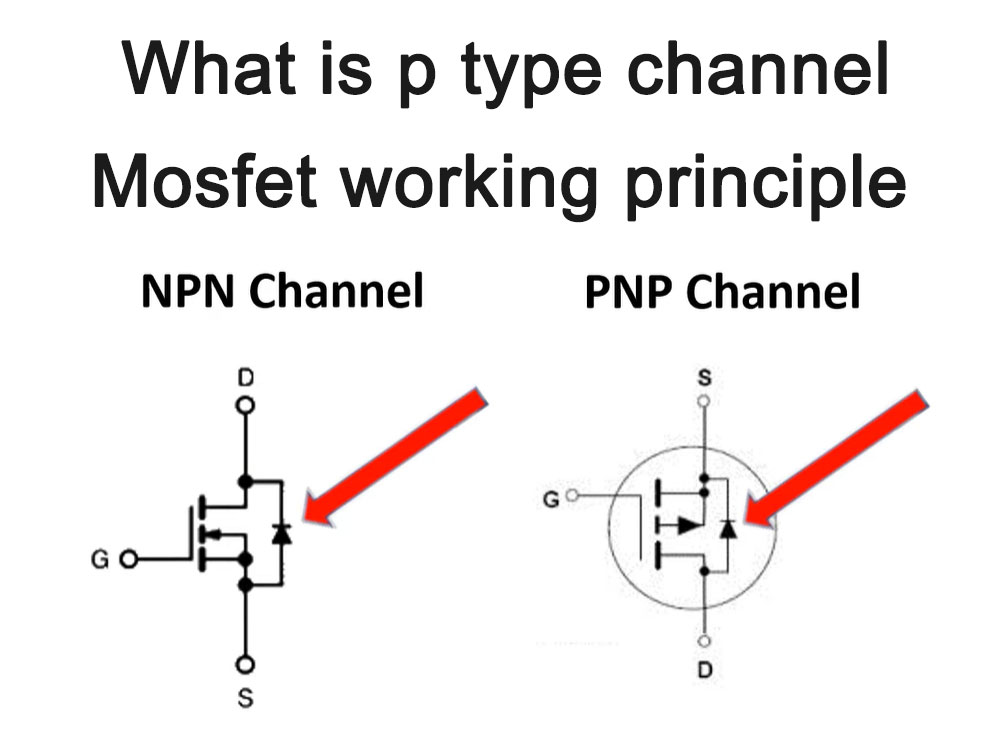
The working principle of P-channel Mosfet is to control the on-off of the channel through the gate voltage, thereby controlling the current between the drain and source.
When the gate voltage is positive, the holes in the P-type semiconductor will be repelled, resulting in a reduction in the number of holes in the channel, so that current cannot flow from the source to the drain, and the MOSFET is in a cut-off state.
When the gate voltage is zero or negative, the number of holes in the channel increases, forming a P-type channel, allowing current to flow from source to drain through the MOSFET, and the MOSFET is in a conductive state.
What is P-type channel MOSFET
P-channel MOSFET is an electronic device whose structure and working principle are similar to N-channel MOSFET, but the charge carriers are holes instead of electrons. In a P-channel MOSFET, holes are the main charge carriers and they flow between the source and drain, controlled by the gate.
The advantages of P-channel MOSFET include high switching speed, low on-resistance and high driving voltage, making it suitable for high-speed digital signal processing systems, communication systems, power electronics and power semiconductors.
P-channel MOSFET is a new generation of high-performance semiconductor devices in recent years, which combines MOSFET and p-channel technology. It has the advantages of MOSFET, such as high control accuracy, small size, low power consumption, high voltage resistance, and low thermal effect.
P-channel Enhancement Mosfet Characteristics
P-channel MOS tube parameter explanation
① Turn-on voltage VGS(th) (or VT)
The turn-on voltage is a parameter of the MOS enhancement type tube. If the gate-source voltage is less than the absolute value of the turn-on voltage, the field effect tube cannot be turned on.
② Pinch-off voltage VGS(off) (or VP)
Pinch-off voltage is a parameter of depletion mode FET. When VGS=VGS(off), the drain current is zero
③ Saturated drain current IDSS
Depletion mode field effect transistor, the corresponding drain current when VGS=0
④ Input resistance RGS
The typical value of the gate-source input resistance of a field effect transistor. For a junction field effect transistor, RGS is approximately greater than 107Ω when reverse biased. For an insulated gate field effect transistor, RGS is approximately 109~1015Ω.
⑤ Low frequency transconductance gm
Low-frequency transconductance reflects the control effect of gate voltage on drain current, which is very similar to the control effect of electron tube. gm can be obtained from the transfer characteristic curve, the unit is mS (milliSiemens)
⑥ Maximum drain power consumption PDM
The maximum drain power dissipation can be determined by PDM = VDS ID, which is equivalent to the PCM of a bipolar transistor.
Frequently Asked Questions about P-Channel MOSFETs
The structure of P-channel MOSFET is similar to that of N-channel MOSFET. The main difference lies in the polarity of its channel. In a P-channel MOSFET, the channel is P-type, the source is P-type, and the drain is N-type.
The working principle of P-channel MOSFET is similar to that of N-channel MOSFET. When the gate voltage is negative, a P-type channel forms, allowing current to flow from source to drain. When the gate voltage is positive, the channel disappears and current cannot pass.
The characteristics of P-channel MOSFET include high switching speed, low on-resistance, high driving voltage, etc. In addition, because the polarity of its channel is P-type, it has higher reliability and stability in certain applications.
P-channel MOSFETs have the opposite source and drain than N-channel MOSFETs, so polarity can be identified by marking or color coding. Typically, the source and drain are marked with the letters “S” and “D”, while the gate is marked with a “G”. In addition, some P-channel MOSFETs also have reverse-blocking diodes, which can be identified by measuring the forward resistance of the diode.
P-channel MOSFETs are widely used in various fields, including consumer electronics, communications, industrial control, automotive electronics, etc. In audio equipment, P-channel MOSFETs are often used in power amplifiers, speaker drivers, etc.; in the automotive field, P-channel MOSFETs are used in automotive motor control, safety systems, etc.